The English and Romanian Adoptees (ERA) study addresses one of the most fundamental questions in developmental psychology and psychiatry – how does early experience shape individual development?
Principal investigator, Professor Edmund Sonuga-Barke from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience
06 January 2020
Severe childhood deprivation has longstanding impacts on brain size in adulthood
Researchers from King’s College London have shown that the brains of young adult Romanian adoptees who were institutionalised as children are around 8.6% smaller than the brains of English adoptees who have not suffered this form of deprivation.

According to the research, the longer the time the Romanian adoptees spent in the institutions, the smaller the total brain volume, with each additional month of deprivation associated with a 0.27% reduction in total brain volume. Deprivation related changes in brain volume were associated with lower IQ and more symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), the study analysed the MRI brain scans of 67 young adults, aged 23-28 years, who were exposed to severely depriving conditions in Romanian institutions under the Communist regime and subsequently adopted into nurturing families in the UK. They were compared to the MRI brain scans of 21 English adoptees aged 23-26 years who had not suffered this institutional deprivation.
MRI scans were conducted at the Centre for Neuroimaging Sciences at King’s College London, as part of the Medical Research Council (MRC) funded English and Romanian Adoptees Brain Imaging Study (ERABIS). This is part of the larger ERA project that has collected information from Romanian and English adoptees over time including measures of mental health and cognitive performance.
Statistical analysis showed that, in this group of young Romanian adults, those changes in brain volume that were related to deprivation were also associated with lower IQ and more ADHD symptoms. This implies that changes in brain structure could play a mediating role between the experience of deprivation and levels of cognitive performance and mental health.
The research investigated other possible factors that could have influenced the results but found the results were unaffected by level of nutrition, physical growth and genetic predisposition for smaller brains.
The principal investigator of the study, Professor Edmund Sonuga-Barke from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN), King’s College London said: ‘The English and Romanian Adoptees (ERA) study addresses one of the most fundamental questions in developmental psychology and psychiatry – how does early experience shape individual development? It’s essential to recognise that these young people have nearly always received great care in loving adoptive families since they left the institutions. However, despite a lot of positive experiences and achievements there remain some deep-seated effects of deprivation on these young adults.’
Showing these very profound effects of early deprivation on brain size and then showing that this difference is associated with low IQ and greater ADHD symptoms provides some of the most compelling evidence of the neuro-biological basis of these problems following deprivation
First author, Dr Nuria Mackes from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience
First author, Dr Nuria Mackes from the IoPPN said: ‘Previous research on the English and Romanian Adoptees (ERA) study has suggested that the emergence and persistence of low IQ and a high level of ADHD symptoms involves structural changes in the brain but, until now, we have not been able to provide direct evidence of this. Showing these very profound effects of early deprivation on brain size and then showing that this difference is associated with low IQ and greater ADHD symptoms provides some of the most compelling evidence of the neuro-biological basis of these problems following deprivation.’
The study also investigated where these changes were occurring in the brain and what localised features contributed to the differences. In comparison to the UK adoptees, the young Romanian adults who had suffered deprivation as children had markedly smaller right inferior frontal regions of the brain both in terms of volume and surface area.
In contrast the right inferior temporal lobe was larger in volume and surface area and thickness for the Romanian young adults and this was associated with lower levels of ADHD symptoms. This implies that this increase in volume and surface area in this region may play a compensatory role in preventing development of ADHD symptoms. In the right medial prefrontal region, the longer the duration of deprivation, the larger the volume and surface area.
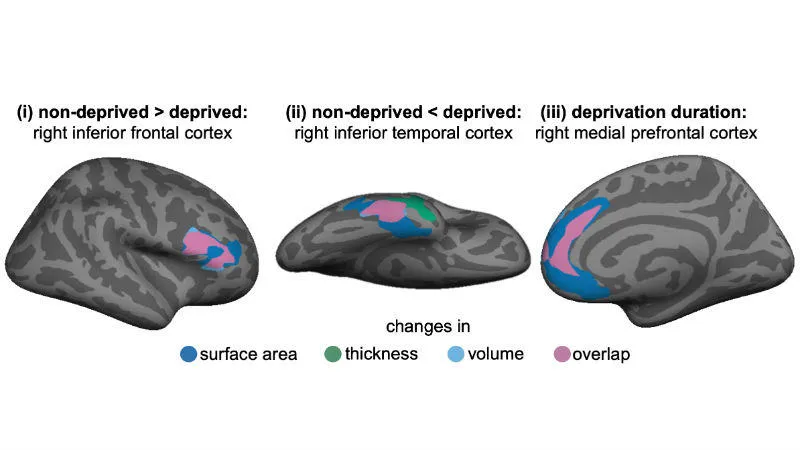
The neuroimaging lead for the study, Professor Mitul Mehta from the IoPPN said: ‘We found structural differences between the two groups in three regions of the brain. These regions are linked to functions such as organisation, motivation, integration of information and memory. It’s interesting to see the right inferior temporal lobe is in fact larger in the Romanian young adults and that this was related to fewer ADHD symptoms, suggesting that the brain can adapt to reduce the negative effects of deprivation. This may explain why some individuals appear less affected than others by deprivation. We believe this is the first time that research has shown such compelling evidence of compensatory effects around deprivation.’
It’s interesting to see the right inferior temporal lobe is in fact larger in the Romanian young adults and that this was related to fewer ADHD symptoms, suggesting that the brain can adapt to reduce the negative effects of deprivation. This may explain why some individuals appear less affected than others by deprivation
Neuroimaging lead for the study, Professor Mitul Mehta from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience
The Romanian young adults in the study had entered into institutions in the first few weeks of life, where they were often malnourished with minimal social contact and little stimulation. The time spent in institutions before adoption into families in the UK varied between 3 and 41 months.
Reflecting on the implications of the study Professor Sonuga-Barke said: ‘By investigating the long term impact of deprivation our research highlights the need for a life-span perspective on the provision of any help and support, especially during the transition to adulthood. More speculatively the evidence of neural compensation in the inferior temporal lobe provides encouragement to look for ways that might help the brain adjust to deprivation and to improve outcomes. For example, it would be interesting to see if targeting this area directly through cognitive training might reduce ADHD symptoms.’
The research was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and funded by Medical Research Council, Economic and Social Research Council and NIHR Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre.
Reference: ‘Early childhood deprivation is associated with alterations in adult brain structure despite subsequent environmental enrichment’ by Mackes et al. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS) DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1911264116
Contact: For interviews or any further media information please contact: Franca Davenport, Interim Senior Press Officer, Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience, King’s College London, franca.davenport@kcl.ac.uk
