
Professor Shanta Persaud
Professor of Diabetes & Endocrinology
- Head, Guy’s Campus Section, School of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Medicine & Sciences
Research interests
- Diabetes
Contact details
Biography
Shanta Persaud is Professor of Diabetes & Endocrinology in the School of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Medicine & Sciences and Head of the Guy’s Campus Section.
She has a first class BSc in Physiology & Pharmacology and a PhD on the regulation of insulin secretion from islets of Langerhans. She lectures on diabetes and endocrinology to BSc students and runs training workshops to MSc and PhD students. Her main research interests lie in investigating ligand interactions with islet G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and signal transduction pathways involved in the secretion of islet hormones and beta-cell mass regulation. Other key areas of research include defining human endocrine pancreas developmental trajectories; cross-talk between metabolically active cells and islets; stimulus-response coupling in human islets. Techniques used by members of her group include isolation of islets from experimental animals; cell culture; measurement of apoptosis by caspase assays; measurement of ATP and NAD(P)H generation; detection of islet cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo by BrdU incorporation into DNA; transient and stable transfection of cells for gene overexpression; CRISPR-mediated gene knockdown; isolation and analysis of RNA and DNA; quantitative RT-PCR; single cell RNA sequencing; spatial transcriptomics; single molecule fluorescence in situ hybridisation; calcium microfluorimetry; dynamic hormone secretion in perifusion; measurement of hormone and cyclic nucleotide levels by immunoassay; investigation of cell-cell interactions and signalling events in cell populations by time-lapse live cell imaging; fluorescence immunocyto/histochemistry; Western blotting of PAGE-fractionated proteins; measurement of serine/threonine and tyrosine kinase activities in situ and in vitro; PRESTO-Tango beta-arrestin recruitment assay for identifying ligand-GPCR interactions; intra-peritoneal glucose and insulin tolerance tests; beta-cell-targeted gene deletion in mice in vivo.
Research

Islet Biology Research Group
Our group studies the fundamental science of islets of Langerhans, from the molecular biology of beta-cells to their effects on whole body physiology. We research the mechanisms of islet dysfunction during type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes, identify novel therapeutic targets, and work to improve islet transplantation therapy for type 1 diabetes.
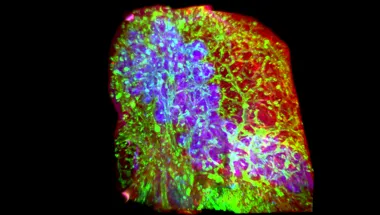
From Developmental Biology to Regenerative Medicine
Understanding organ development and tissue regeneration provides a framework for elucidating disease mechanisms as well as for developing new therapeutics.
News
£4.8 million awarded to King's scientists to help find cure for type 1 diabetes
Two major research projects, led by Professor Shanta Persaud and Dr Aileen King, and Professor Francesca Spagnoli, Dr Rocio Sancho and Professor Molly Stevens...
Potential breakthrough for growing insulin-producing cells in the laboratory
Researchers have analysed the types of cells and genes involved in the development of beta cells in the pancreas responsible for making insulin.

Drug used to treat obesity provides diabetes therapy promise
Researchers from King’s have found that a drug previously used to treat obesity can increase insulin levels in human cells.

Features
5 minutes with Shanta Persaud - International Day of Women and Girls in Science edition
Shanta Persaud is Professor of Diabetes & Endocrinology and Head of the Department of Diabetes in the School of Life Course Sciences

Research

Islet Biology Research Group
Our group studies the fundamental science of islets of Langerhans, from the molecular biology of beta-cells to their effects on whole body physiology. We research the mechanisms of islet dysfunction during type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes, identify novel therapeutic targets, and work to improve islet transplantation therapy for type 1 diabetes.

From Developmental Biology to Regenerative Medicine
Understanding organ development and tissue regeneration provides a framework for elucidating disease mechanisms as well as for developing new therapeutics.
News
£4.8 million awarded to King's scientists to help find cure for type 1 diabetes
Two major research projects, led by Professor Shanta Persaud and Dr Aileen King, and Professor Francesca Spagnoli, Dr Rocio Sancho and Professor Molly Stevens...

Potential breakthrough for growing insulin-producing cells in the laboratory
Researchers have analysed the types of cells and genes involved in the development of beta cells in the pancreas responsible for making insulin.

Drug used to treat obesity provides diabetes therapy promise
Researchers from King’s have found that a drug previously used to treat obesity can increase insulin levels in human cells.

Features
5 minutes with Shanta Persaud - International Day of Women and Girls in Science edition
Shanta Persaud is Professor of Diabetes & Endocrinology and Head of the Department of Diabetes in the School of Life Course Sciences

