
Dr Ciro Chiappini
Reader in BioNano Engineering
- Associate Dean for Impact
Biography
Ciro Chiappini is a BioNano Engineer specialising in nanofabrication, biointerface design, and cell manipulation. He graduated in Physics from the University of Milan (2006) and completed his PhD in Biomedical Engineering at the University of Texas at Austin in 2011. His postdoctoral research career at Imperial College London was supported by a Royal Society Newton International Fellowship and a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Fellowship.
He joined King’s College London in 2016 as Lecturer and is now Reader and Associate Dean for Impact in the Faculty of Dentistry, Oral and Craniofacial Sciences.
Dr Chiappini’s research focuses on developing medtech solutions for advanced therapies and precision diagnostics. He has authored more than 70 publications in leading peer-reviewed journals, including Nature Nanotechnology, Nature Materials, Nature Protocols, Nature Reviews Materials, Advanced Materials, PNAS, and ACS Nano, and is an inventor on five patents. His work has been funded by the European Research Council, the Royal Society, UKRI, industry partners, and several charities, for a total exceeding £3 million.
Research
Centre for Craniofacial & Regenerative Biology
Our research goes beyond the mouth. If we understand how the entire face and head forms, we can repair damage and regenerate cells. If we unravel the causes of diseases, we can treat patients successfully. If we solve these problems, our discoveries will improve health worldwide.
Chiappini Lab
Nanotechnology, bioengineering and cell biology to develop functional materials that direct cell behaviour, for applications in regenerative and precision medicine.
Regenerative Biomaterials
Regenerative biomaterials are an essential component in developing advanced cell and gene therapies for tissue regeneration. The Centre for Craniofacial & Regenerative Biology is at the forefront of regenerative biomaterials discovery and translation, thanks to unique synergies arising from leading expertise in developmental biology, bioengineering and cell technologies.
Physiological Oxygen Laboratory
Cardiovascular - Physiological Oxygen Laboratory

Prenatal ThERapy for SIckle CelL disEaSe (PERICLES)
To generate new knowledge about stakeholders' views on prenatal therapy for Sickle Cell Disease, identify ethical issues and establish protocols for support.
Project status: Ongoing
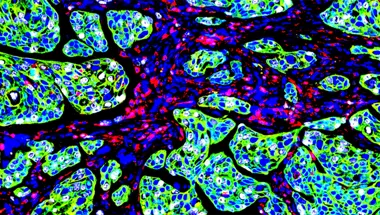
Spatial Biology Network
The Spatial Biology Network is a cross-faculty research interest group that brings together researchers from various disciplines, ranging from technology development and molecular biology, to bioinformatics and clinical translational research, to explore the complexity of spatial biology.

Immunometabolism (iMet) Research Interest Group (RIG)
The aim of the i-met research interest group is to stimulate novel collaborations in the field of Immunometabolism, a young but rapidly growing field of research.

BHF 4-yr PhD Programme: Next Generation Human Models of Cardiovascular Disease
This 4-year PhD programme is the first in the UK dedicated exclusively to in vitro, ex vivo and in silico human models of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
News
Tens of millions of nanoneedles could replace painful cancer biopsies
A patch containing tens of millions of microscopic nanoneedles could soon replace traditional biopsies, scientists have found.
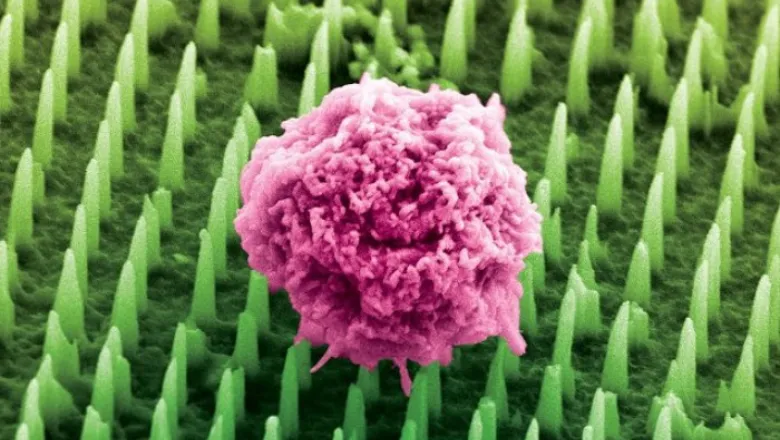
A Scalable Method for Engineering Therapeutic Immune Cells
A collaboration between the Centre for Craniofacial and Regenerative Biology and the Peter Gorer Department of Immunobiology at King’s College London has...

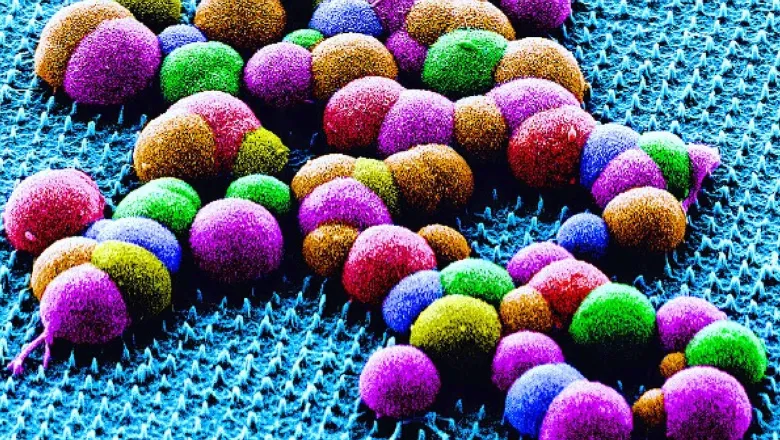
Nanoneedle Technology Corrects Genetic Mutation in Rare Skin Disease
Researchers from the Faculty of Dentistry, Oral & Craniofacial Sciences at King’s College London have developed a novel technique using tiny, biocompatible...

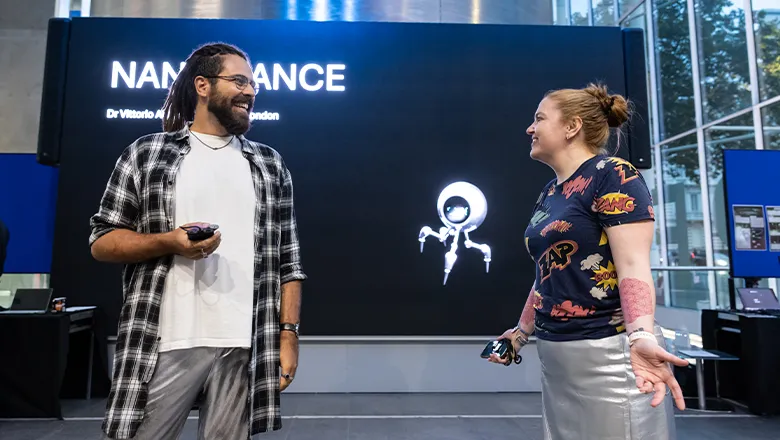
Celebrating Nano for Humanity: How Tiny Science is Shaping Our Future
The Nano for Humanity event, from the London Centre for Nanotechnology (LCN), brought together physicists from King's College London, Imperial College London...

Academic Promotions
Congratulations to the following members of the Faculty of Dentistry, Oral & Craniofacial Sciences who were awarded academic promotions.

Events

Centre for the Physical Science of Life Symposium 2025
Please join us in-person for the Centre for the Physical Science of Life Symposium at King’s College London.
Please note: this event has passed.
Research

Centre for Craniofacial & Regenerative Biology
Our research goes beyond the mouth. If we understand how the entire face and head forms, we can repair damage and regenerate cells. If we unravel the causes of diseases, we can treat patients successfully. If we solve these problems, our discoveries will improve health worldwide.

Chiappini Lab
Nanotechnology, bioengineering and cell biology to develop functional materials that direct cell behaviour, for applications in regenerative and precision medicine.

Regenerative Biomaterials
Regenerative biomaterials are an essential component in developing advanced cell and gene therapies for tissue regeneration. The Centre for Craniofacial & Regenerative Biology is at the forefront of regenerative biomaterials discovery and translation, thanks to unique synergies arising from leading expertise in developmental biology, bioengineering and cell technologies.

Physiological Oxygen Laboratory
Cardiovascular - Physiological Oxygen Laboratory

Prenatal ThERapy for SIckle CelL disEaSe (PERICLES)
To generate new knowledge about stakeholders' views on prenatal therapy for Sickle Cell Disease, identify ethical issues and establish protocols for support.
Project status: Ongoing

Spatial Biology Network
The Spatial Biology Network is a cross-faculty research interest group that brings together researchers from various disciplines, ranging from technology development and molecular biology, to bioinformatics and clinical translational research, to explore the complexity of spatial biology.

Immunometabolism (iMet) Research Interest Group (RIG)
The aim of the i-met research interest group is to stimulate novel collaborations in the field of Immunometabolism, a young but rapidly growing field of research.

BHF 4-yr PhD Programme: Next Generation Human Models of Cardiovascular Disease
This 4-year PhD programme is the first in the UK dedicated exclusively to in vitro, ex vivo and in silico human models of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
News
Tens of millions of nanoneedles could replace painful cancer biopsies
A patch containing tens of millions of microscopic nanoneedles could soon replace traditional biopsies, scientists have found.

A Scalable Method for Engineering Therapeutic Immune Cells
A collaboration between the Centre for Craniofacial and Regenerative Biology and the Peter Gorer Department of Immunobiology at King’s College London has...

Nanoneedle Technology Corrects Genetic Mutation in Rare Skin Disease
Researchers from the Faculty of Dentistry, Oral & Craniofacial Sciences at King’s College London have developed a novel technique using tiny, biocompatible...

Celebrating Nano for Humanity: How Tiny Science is Shaping Our Future
The Nano for Humanity event, from the London Centre for Nanotechnology (LCN), brought together physicists from King's College London, Imperial College London...

Academic Promotions
Congratulations to the following members of the Faculty of Dentistry, Oral & Craniofacial Sciences who were awarded academic promotions.

Events

Centre for the Physical Science of Life Symposium 2025
Please join us in-person for the Centre for the Physical Science of Life Symposium at King’s College London.
Please note: this event has passed.
